You're planning a campaign, and the data you need is scattered across six different systems. Your email platform says one thing about a customer. Your loyalty program says another. Your paid media team is working from a list that doesn't match either one. By the time you launch, you're not entirely sure who you're reaching or whether the message will land.
This is the reality for most marketing teams. Not because they lack data, but because that data doesn't work together.
A 360-degree view of your customers changes that equation. It's a unified, always-current view of every customer that powers better marketing decisions. Not just a database or a dashboard, but the foundation that lets you know who your customers really are, predict what they'll do next, and reach them in the channels where they're most responsive.
This guide covers what a true customer 360 looks like, the barriers that get in the way, and how modern AI-powered solutions make it achievable.
What is a 360-degree view of your customers?
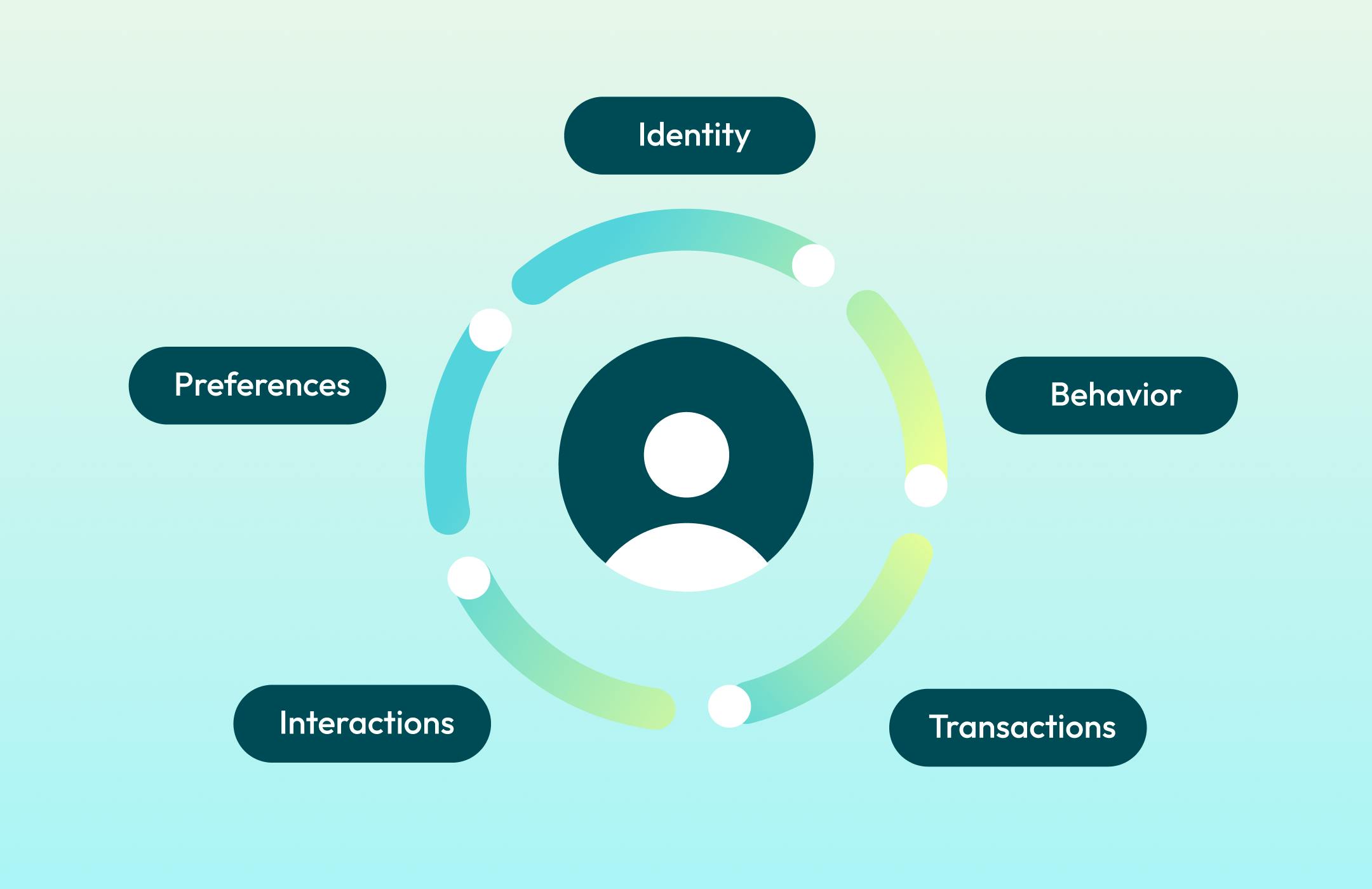
A 360-degree customer view is a single, unified profile that brings together everything you know about each customer across every touchpoint and system. It's the difference between having data about customers and actually understanding them.
A complete customer 360 includes five core components:
Identity: Who they are across all your systems, resolved into a single record
Behavior: What they do across channels, from website visits to store purchases
Preferences: How they want to engage, including channel and communication preferences
Transactions: Their complete purchase history and customer value
Interactions: Service contacts, support tickets, loyalty activity, and engagement signals
The key distinction is between data aggregation and true unification. Aggregation means you've collected customer data in one place. Unification means you've connected those records to actual individuals. Most brands have far more customer records than actual customers because the same person appears as five or ten separate entities across different systems. A true 360-degree view resolves that fragmentation.
Why a 360-degree customer view matters
Customer expectations have shifted dramatically. Research from McKinsey shows that 71% of consumers expect companies to deliver personalized interactions, and 76% get frustrated when this doesn't happen. Companies that excel at personalization generate 40% more revenue from those efforts than their slower-growing competitors.
But personalization at scale is impossible when your data is fragmented. You end up targeting the same customer multiple times with conflicting messages, wasting ad spend on duplicate records, and delivering experiences that feel disjointed rather than seamless.
The business impact of unified customer data shows up across multiple dimensions. Marketing efficiency improves because you're not paying to reach the same person as five separate records. Customer lifetime value increases because you can identify and nurture your most valuable relationships. Retention improves because you can spot churn signals early and intervene. And measurement becomes meaningful because you can attribute outcomes to actual individuals rather than fragmented identities.
Several trends make this urgent. Third-party cookies are disappearing. Privacy regulations require unified data management. And competitive pressure is mounting from brands that have already solved this problem.
Common barriers to achieving customer 360
If building a 360-degree customer view were easy, everyone would have one. Several challenges make this difficult in practice.
Data silos across departments and systems. Customer data comes from everywhere: CRM, transaction platforms, loyalty programs, marketing automation, customer service, mobile apps, and more. Each system captures a piece of the customer relationship, but none have the complete picture. Your CRM shows one view. Your email platform shows another. Your paid media team works from something different entirely.
Identity resolution challenges. Customers don't make unification easy. They use different email addresses for different purposes. They move and change phone numbers. They share devices with family members. They make purchases as guests without logging in. One person might have dozens of identifiers scattered across your systems, with no obvious way to connect them.
Data quality and consistency issues. Even when you can identify the same person across systems, the data often conflicts. Name variations (Bob vs. Robert), address formatting inconsistencies, outdated contact information, and incomplete records all complicate the matching process.
Privacy and compliance considerations. GDPR, CCPA, and evolving state regulations require careful handling of customer data. Unification needs to happen in a way that respects consent preferences and supports compliance requirements.
Technical debt and legacy systems. Many organizations have existing infrastructure that wasn't designed for unification. Manual processes, IT backlogs, and batch-oriented architectures slow progress and limit what's possible.
Key components of a 360-degree customer view
Building a true customer 360 requires several interconnected capabilities working together.
Identity resolution and customer matching. This is the foundation. Identity resolution connects records across systems by matching on identifiers like email, phone, address, and device IDs. The best approaches combine deterministic matching (exact matches on known identifiers) with probabilistic matching (AI-powered connections that handle variations and incomplete data). The output is a stable, unique identifier for each customer that persists even as their contact information changes.
Data integration from all touchpoints. A complete view requires data from online channels (web, mobile, email, paid media), offline channels (point-of-sale, call center, direct mail), and third-party sources (partner data, enrichment). The more sources connected, the more complete the profile.
Real-time data synchronization. Batch processing handles historical data, but customers don't wait for overnight refreshes. Real-time capabilities enable triggered campaigns, instant segmentation based on recent events, and live personalization that responds to in-the-moment behavior.
Predictive attributes and AI-driven insights. Historical data tells you what customers have done. Predictive models tell you what they're likely to do next: their probability of purchasing, expected lifetime value, churn risk, and product affinities. This shifts marketing from reactive to proactive.
Activation capabilities across channels. A customer 360 is only valuable if you can act on it. Native connections to email platforms, paid media, personalization tools, and data infrastructure ensure that unified profiles translate into better campaigns.
How to build a 360-degree view: a step-by-step process
The path from fragmented data to unified customer profiles follows a logical progression.
Step 1: Audit your current customer data sources. Start by inventorying every system that touches customer data. Identify which fields exist where, which identifiers are available, and where the gaps are. This assessment reveals the scope of what needs to be connected.
Step 2: Define your single source of truth strategy. When records conflict, which attributes take priority? Establishing merge policies upfront prevents confusion later. Decide how you'll handle cases where different systems show different email addresses, phone numbers, or preferences for the same customer.
Step 3: Implement identity resolution. This is where fragmented records become unified profiles. AI-powered approaches handle the messiness of real-world data: typos, variations, missing fields, and changing information. Deterministic matching provides exact matches for operational use cases that require precision.
Step 4: Establish data governance and quality standards. Consistent field definitions (semantic tagging) ensure that "email" means the same thing across all sources. Ongoing quality monitoring catches issues before they impact campaigns.
Step 5: Create unified customer profiles. With identity resolved and governance in place, build the Customer 360 database with the attributes you need: demographics, transaction history, engagement signals, and predictive scores.
Step 6: Enable activation across marketing systems. Configure connections to your downstream tools. Test audience delivery and validate match rates to ensure your unified data translates into better targeting.
Step 7: Measure and optimize continuously. Use control groups and experimentation to prove impact. Track campaign performance against unified profiles. Iterate on segmentation and targeting based on what works.
The role of AI in modern customer 360 solutions
Traditional rule-based approaches to identity resolution work for exact matches but struggle with the messiness of real-world customer data. When a customer uses "Bob" in one system and "Robert" in another, or when they move and update their address in some systems but not others, rigid rules fail.
AI-powered identity resolution changes what's possible. Machine learning models trained on massive historical matching datasets can handle variations, typos, missing fields, and changing information. They assign confidence scores to each potential match, finding hidden connections across online and offline data that rule-based systems miss.
Beyond identity resolution, AI enables predictive customer attributes that transform how marketers work. Predicted customer lifetime value estimates the total value each customer will generate over the next year, combining probability of purchase, expected order frequency, and average order value. Churn propensity models identify customers whose purchase patterns are declining before they're lost. Product affinity predictions power cross-sell and upsell campaigns with relevant recommendations.
AI also accelerates implementation. Modern platforms use AI to automatically infer which fields contain personal information, suggest optimal matching configurations, and identify data quality issues. What used to take months of manual configuration can now happen in weeks.
The result is accuracy at scale that wasn't previously achievable. Profiles are more complete, match rates are higher, and predictions are more reliable.
Customer 360 use cases across industries
While the fundamentals apply everywhere, specific applications vary by industry.
Retail teams use customer 360 for omnichannel personalization, connecting online browsing behavior with in-store purchases. Loyalty program optimization becomes possible when you can see each member's complete relationship, not just their program activity. And ad spend becomes more efficient when you're targeting actual individuals rather than duplicate records.
Financial services organizations benefit from complete customer views for both compliance and experience. Risk assessment improves with full relationship visibility. Customer service teams can see the complete picture when helping clients. And product recommendations become relevant when based on the full relationship rather than siloed transaction data.
Travel and hospitality brands use unified profiles for guest recognition across properties and channels. Real-time personalization during booking and stay becomes possible. And ancillary revenue optimization improves when you understand each traveler's preferences and history.
Media and entertainment companies apply customer 360 to subscriber engagement, connecting cross-platform viewing behavior and preventing churn with predictive lifecycle signals.
Choosing the right technology: CDP evaluation criteria
Not all customer data platforms deliver the same capabilities. When evaluating solutions, focus on these criteria.
Identity resolution capabilities. Does the platform handle both probabilistic and deterministic matching? How does it manage identity stability over time as customer information changes?
Data integration breadth. Look for native connectors to your existing systems. Evaluate support for both batch and real-time data ingestion.
AI and predictive capabilities. Are predictive models built in, or do they require custom development? Can marketers access insights directly, or does everything require data science resources?
Privacy and compliance features. How does the platform handle consent management and data governance? Does it support requirements for GDPR, CCPA, and emerging regulations?
Time to value and ease of implementation. Look for out-of-the-box models and templates that accelerate deployment. Self-service capabilities for marketers reduce dependence on technical teams.
Scalability and activation speed. Evaluate performance at your data volumes. Consider campaign refresh rates and real-time capabilities for time-sensitive use cases.
Best practices for maintaining your customer 360
Building a customer 360 is a milestone, not a finish line. Maintaining data quality and value requires ongoing attention.
Establish a data governance framework with clear ownership, documented policies, and defined stewardship roles. Without governance, data quality degrades over time.
Conduct regular data quality audits to benchmark profile accuracy and catch issues early. Monitor for identity instability where profile assignments change unexpectedly.
Foster cross-functional collaboration between marketing, IT, analytics, and customer service. Shared definitions and success metrics keep everyone aligned on what the customer 360 is supposed to deliver.
Maintain privacy-first data practices by minimizing collection to what's genuinely needed and honoring consent preferences across all activation.
Optimize continuously based on business outcomes. Measure campaign performance against unified profiles. Iterate on segmentation strategies. Let results guide refinement.
Conclusion
Customer data has always been important. But for too long, that data has been locked in silos, fragmented across systems, and difficult to act on. Marketers have been forced to work around their data instead of with it.
A 360-degree view of your customers changes that equation. When your data is unified, accurate, and connected to the tools you use every day, you can finally focus on what marketing is supposed to be: building relationships, creating value, and driving growth.
The complexity of identity resolution, data integration, and predictive modeling can be handled by modern AI-powered platforms. What remains is the opportunity to market smarter, move faster, and deliver the experiences your customers expect.
Ready to see what a unified customer view can do for your team? Request a demo to learn how Amperity helps enterprises build their customer 360 with AI-powered identity resolution.
Customer 360 FAQs
What is the difference between a customer 360 and a CDP?
A customer 360 is the outcome: a unified, complete view of each customer. A customer data platform (CDP) is one way to achieve that outcome. CDPs specialize in collecting data from multiple sources, resolving customer identity, and activating unified profiles across marketing channels. Think of the customer 360 as the destination and the CDP as the vehicle.
How long does it take to implement a customer 360?
Timelines vary based on data complexity and organizational readiness. With a modern CDP that includes AI-powered identity resolution and pre-built models, many enterprises move from data connection to initial activation in weeks rather than months. Automated semantic tagging and out-of-the-box predictive models are key accelerators.
What data sources are needed for a 360-degree customer view?
A complete customer 360 typically includes transaction data (purchases, orders), behavioral data (web, mobile, email engagement), CRM and service data, loyalty program data, and marketing interaction history. Start with core systems and expand over time. The more sources connected, the more complete the profile.
How does identity resolution work?
Identity resolution connects customer records across systems by matching on identifiers like email, phone, address, and device IDs. AI-powered approaches use probabilistic matching to handle variations, misspellings, and changing information. Deterministic matching provides exact matches for operational use cases requiring precision. The output is a stable identifier for each unique customer.
What is the ROI of a customer 360 initiative?
ROI typically comes from reduced marketing waste (eliminating duplicate records), improved ad match rates, higher conversion through personalization, and better retention through churn prevention. Companies with mature customer 360 capabilities report improved campaign performance, higher customer lifetime value, and more efficient ad spend across channels.
How do you maintain data quality in a customer 360?
Ongoing data quality requires governance frameworks, regular audits, and monitoring tools. Modern CDPs include quality benchmarking that tracks profile accuracy over time and alerts teams to issues before they impact business outcomes. Cross-functional collaboration ensures consistent standards across the organization.
Can a customer 360 work with real-time data?
Yes. While batch processing handles historical data, real-time capabilities enable triggered campaigns, instant segmentation based on recent events, and live personalization. Look for solutions that support both batch and streaming data to balance historical depth with in-the-moment responsiveness.